Actor portrayals.
Study Design
The ATTRibute-CM study evaluated the impact
of Attruby on survival, hospitalization, and
health-related quality of life1,2
ATTRibute-CM was a prospective, multicenter, international,
randomized (2:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled study in
611 patients with ATTR-CM1,2*
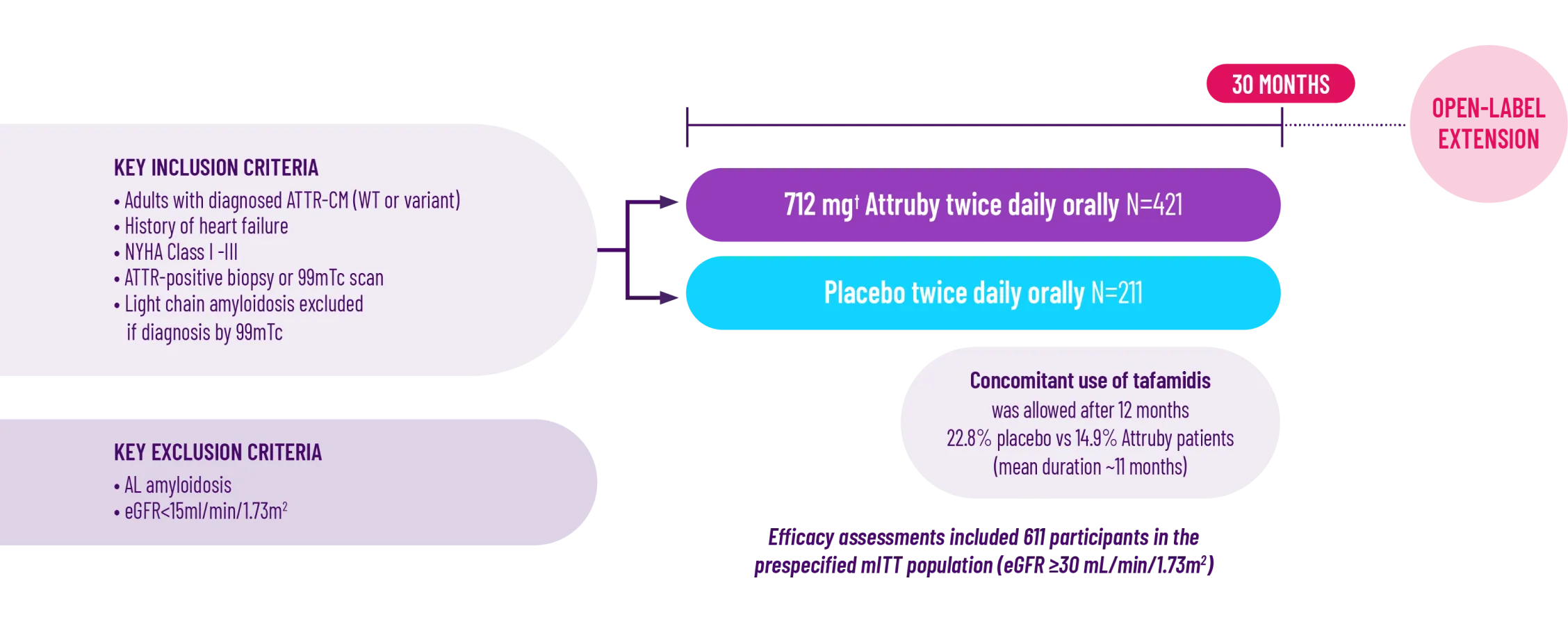
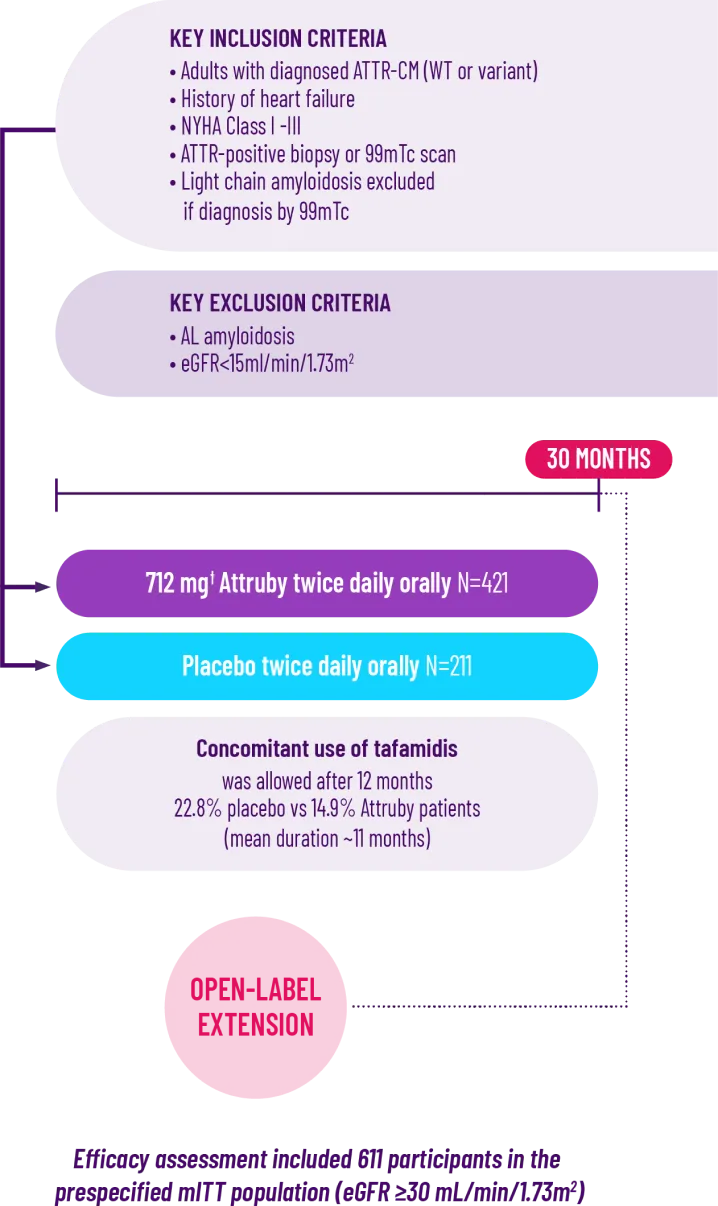
*A total of 632 patients underwent randomization. Of these patients, 21 who had stage 4 CKD were excluded from the primary analysis in the mITT population.2
†Attruby 712 mg twice daily is equivalent to Attruby HCl 800 mg twice daily.3
The ATTRibute-CM study evaluated the impact of Attruby on mortality, hospitalization, and health-related quality of life over 30 months
Primary Endpoint 1,2‡
was a hierarchical composite of:
- ACM
- Cumulative frequency of CVH
- Change from baseline in NT-proBNP
- Change from baseline in 6MWD
Secondary Endpoints2,3
were individual assessments of:
Key secondary endpoints
- Change from baseline in 6MWD
- Change from baseline in KCCQ-OS
- Change from baseline in serum TTR
- ACM
Other secondary endpoints
- CVM§
- Cumulative frequency of CVH§
- Change from baseline in NT-proBNP§
- Safety assessments||
Primary Endpoint 1,2‡
was a hierarchical composite of:
- ACM
- Cumulative frequency of CVH
- Change from baseline in NT-proBNP
- Change from baseline in 6MWD
Secondary Endpoints2,3
were individual assessments of:
Key secondary endpoints
- Change from baseline in 6MWD
- Change from baseline in KCCQ-OS
- Change from baseline in serum TTR
- ACM
Other secondary endpoints
- CVM§
- Cumulative frequency of CVH§
- Change from baseline in NT-proBNP§
- Safety assessments||
‡Analysis conducted using the stratified F-S test.1
§These secondary endpoints are prespecified and non-alpha protected.3,4
||Based on ITT population of 632 patients, including 21 who had stage 4 CKD. The ITT population was defined as all randomized participants who received at least 1 dose of study drug and had at least 1 postbaseline efficacy evaluation and included participants who had a baseline eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2.2
Attruby was studied
in a contemporary
ATTR-CM population
that
reflects recent approaches
in diagnosis and care2,4
The proportion of trial participants
in the earlier stages of disease¶
reflects changes
in disease
recognition and management
in recent years2,4
| mITT Population Characteristic3 |
Attruby n=409 |
Placebo n=202 |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | ||
| Mean (standard deviation) | 77.32 (6.474) | 76.96 (6.739) |
| Sex, % (n) | ||
| Male | 91.4% (374) | 89.6% (181) |
| Female | 8.6% (35) | 10.4% (21) |
| TTR Genotype,# % (n) | ||
| ATTRv | 9.5% (39) | 9.9% (20) |
| ATTRwt | 90.5% (370) | 90.1% (182) |
| NYHA Class, % (n) | ||
| NYHA Class I | 12.5% (51) | 8.4% (17) |
| NYHA Class II | 70.4% (288) | 77.2% (156) |
| NYHA Class III | 17.1% (70) | 14.4% (29) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2), % (n) | ||
| >45 | 84.1% (344) | 85.6% (173) |
| ≤45 | 15.9% (65) | 14.4% (29) |
mITT Population Characteristic5
Attruby n=409
Placebo n=202
-
Age, years
-
-
Mean (standard deviation)
77.32 (6.474)
76.96 (6.739)
-
-
Sex, % (n)
-
-
Male
91.4% (374)
89.6% (181)
-
Female
8.6% (35)
10.4% (21)
-
-
TTR Genotype,# % (n)
-
-
ATTRv
9.5% (39)
9.9% (20)
-
ATTRwt
90.5% (370)
90.1% (182)
-
-
NYHA Class, % (n)
-
-
NYHA Class I
12.5% (51)
8.4% (17)
-
NYHA Class II
70.4% (288)
77.2% (156)
-
NYHA Class III
17.1% (70)
14.4% (29)
-
-
eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2), % (n)
-
-
≥45
84.1% (344)
85.6% (173)
-
<45
15.9% (65)
14.4% (29)
-

Attruby was proven to make a positive impact in hospitalizations, quality of life, survival, and more1,2

Low rates of discontinuations due to adverse drug reactions and convenient dosing with Attruby1
¶i.e., NYHA Class I and II.2
#IXRS stratification factors.3
6MWD=6-minute walk distance; 99mTc=technetium labeled pyrophosphate (PYP) or bisphosphonate (eg, DPD); ACM=all-cause mortality; AE=adverse event; AL amyloidosis=light chain amyloidosis; ATTR-CM=transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy; ATTRv=hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis; ATTRwt=transthyretin amyloidosis wild-type; CKD=chronic kidney disease; CV=cardiovascular; CVH=cardiovascular-related hospitalization; CVM=cardiovascular-related mortality; eGFR=estimated glomerular filtration rate; F-S test=Finkelstein-Schoenfeld test; GI=gastrointestinal; IXRS=Interactive Web Response Systems; KCCQ-OS=Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire Overall Summary; mITT=modified intent-to-treat NT-proBNP=N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide; NYHA=New York Heart Association; TTR=transthyretin; WT=wild-type.
References: 1. Attruby. Prescribing information. BridgeBio, Inc.; 2024.
2. Gillmore JD, Judge DP, Cappelli F, et al. Efficacy and safety of acoramidis in transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(2):132-142. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2305434
3. Data on file. BridgeBio, Inc.; 2024.
4. Ioannou A, Patel RK, Razvi Y, et al. Impact of earlier diagnosis in cardiac ATTR amyloidosis over the course of 20 years. Circulation. 2022;146(22):1657-1670. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.060852
5. Gillmore JD, Judge DP, Cappelli F, et al. Efficacy and safety of acoramidis in transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy [study protocol]. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(2):132-142. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2305434
Indication and Important safety information
INDICATION
Attruby® (acoramidis) is indicated for the treatment of the cardiomyopathy of wild-type or variant transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis (ATTR-CM) in adults to reduce cardiovascular death and cardiovascular-related hospitalization.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Adverse Reactions
Diarrhea (11.6% vs 7.6%) and upper abdominal pain (5.5% vs 1.4%) were
reported in patients treated with Attruby versus placebo,
respectively. The majority of these adverse reactions were mild and
resolved without drug discontinuation.
Discontinuation rates due to adverse events were similar between patients treated with Attruby versus placebo (9.3% and 8.5%, respectively).
Laboratory Tests
Mean increase in serum creatinine of 0.2 and 0.0 mg/dL and a mean
decrease in eGFR of 8.2 and 0.7 mL/min/1.73 m2 was
observed in the
adults with ATTR-CM treated with Attruby versus placebo,
respectively, at Day 28 and then stabilized. These changes were
reversible after treatment discontinuation.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy & Lactation: There are no data on the use of Attruby in pregnant women. Animal data have not shown developmental risk associated with the use of Attruby in pregnancy. There are no available data on the presence of Attruby in either human or animal milk or the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant or maternal milk production.
Please see Full Prescribing Information including Patient Information.
INDICATION AND IMPORTANT
SAFETY INFORMATION
INDICATION
Attruby® (acoramidis) is indicated for the treatment of the cardiomyopathy of wild-type or variant transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis (ATTR-CM) in adults to reduce cardiovascular death and cardiovascular-related hospitalization.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Adverse Reactions
Diarrhea (11.6% vs 7.6%) and upper abdominal pain (5.5% vs 1.4%) were
reported in patients treated with Attruby versus placebo,
respectively. The majority of these adverse reactions were mild and
resolved without drug discontinuation.
Discontinuation rates due to adverse events were similar between patients treated with Attruby versus placebo (9.3% and 8.5%, respectively).
Laboratory Tests
Mean increase in serum creatinine of 0.2 and 0.0 mg/dL and a mean
decrease in eGFR of 8.2 and 0.7 mL/min/1.73 m2 was
observed in the
adults with ATTR-CM treated with Attruby versus placebo,
respectively, at Day 28 and then stabilized. These changes were
reversible after treatment discontinuation.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy & Lactation: There are no data on the use of Attruby in pregnant women. Animal data have not shown developmental risk associated with the use of Attruby in pregnancy. There are no available data on the presence of Attruby in either human or animal milk or the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant or maternal milk production.
Please see Full Prescribing Information including Patient Information.

